Google is one of the most influential companies of the information age.
Formally named Alphabet, Google is generally credited as one of the major companies that brought broad, consumer-level success to the internet. Google’s ability to generate reliable searches helped turn the early web from a place of relatively specialized knowledge and limited scope into a broadly available platform that anyone could use.
Today, Google is one of the most valuable companies in the world. The company has more than 50 different lines of business, chiefly in software, online services and technology hardware. The majority of Google’s revenue still comes from its search and advertising businesses, which generate a significant majority of the company’s overall revenue. It currently has a market cap over $2 trillion.
Here’s what you should know.
For financial and economic news that may affect Google and other potential investments, sign up for the Market Minute newsletter.
A Brief History of Google
Google was created in 1996 by founders Sergey Brin and Larry Page. They originally created the search engine as a computer science project called BackRub while graduate students at Stanford University. Their invention, which would eventually become the Google search engine, rested on two main developments.
The first is a concept known as “backlinking,” in which a search would return results based on how many third parties referenced any given source. This was an idea borrowed from the traditional structure of academic citations, in which a work is evaluated in part by how often other papers refer to it.
The second is a process known as “crawling.” This is a software tool that efficiently finds and indexes documents connected to the internet. While these documents are typically posted in the form of web pages, a crawler can find anything publicly accessible on a networked computer.
These two innovations allowed Brin and Page to create Google, a search engine which found pages posted on the internet and organized them based on their strength of third-party references. This was a significant improvement over previous search engines and it led to arguably the first broadly accessible version of the web.
The company Google was founded in 1998. It began with $100,000 in seed funding and launched its operations in a Menlo Park garage. It grew very quickly, and by 1999 had received another $25 million in additional venture capital funds. In 2001, Eric Schmidt joined the company as its CEO, a signal that Google intended to be a serious firm in Silicon Valley.
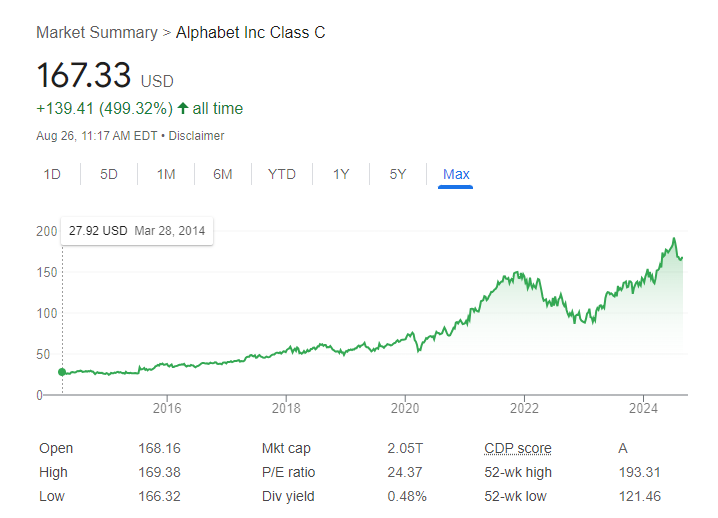
Three years later, on August 19, 2004, Google went public with an initial share price of around $2.50 (split-adjusted). Investments made in 2004 and held through 2024 would yield investors over 6,600%.
A financial advisor can help you build a portfolio based on your goals.
Since then, Google has both diversified and entrenched its business model. The company launched its Gmail service, which quickly became one of the web’s largest email services, and Google News, which many people rely on as their primary (if not only) source of news. Perhaps most notably, Google launched Google Earth and Google Maps in 2005 (services largely developed by the then-acquired firm Keyhole). When paired with the then-emerging smartphone market, this redefined navigation and introduced the era of real time directions for travelers.

In 2006, Google began expanding Gmail into the product currently known as Google Workspace. Today, this includes a suite of workplace and productivity tools that include video conferences, calendars, collaboration and project management software, Google Docs, Google Drive and more.
Google has also launched numerous high-profile acquisitions over the past 20 years. Of those, the most important was Google’s 2007 acquisition of DoubleClick. This was an advertising service that had become one of the largest ad distributors on the internet at the time. Buying this company allowed Google to bring much of its ad business in-house, meaning that Google not only generated ad revenue from its search engine but also for third-party ads run on other websites. This allowed Google to develop its modern business model, where user data from its many different services support the ads that it shows on unrelated websites.
Around the same time (in 2006), Google also acquired YouTube, making the company a dominant presence in video and social media. In 2008, Google also launched its App Engine, a service that would eventually become Google Cloud.
In 2008, Google also expanded into the smartphone market when it acquired Android. This has since become the most popular smartphone OS in the world, and one of the largest tablet operating systems. This expansion allowed Google to launch the Google Play Store in 2012. It followed up in the hardware market with the Google Pixel and the Google Home smart speaker in 2016.
In 2015, to signify its growing range of operations, Google officially reorganized under a new company called Alphabet. The search engine company Google remains a subsidiary of Alphabet.
Currently, Google has invested significantly in artificial intelligence, most notably through the company DeepMind (acquired in 2014). Google has announced several different AI initiatives, including a completely restructured form of search that returns results based on summaries of existing web sites rather than links to those sites. However, like many AI-based firms, Google has faced criticism and some early litigation over charges of plagiarism and intellectual property theft involved with AI summarization results.
The Market Minute Newsletter can help you keep up to date with news that may affect the investment markets.
Google’s Business and Revenue
From a revenue perspective, most of Google’s most significant innovations and acquisitions took place in or around the 2000’s. This is common for many large technology firms and it is a trend that tech investors should be aware of.
Google currently brings in around $84.2 billion per quarter in revenue. Of this revenue, almost all comes from products that have existed for more than 10 years.
Specifically, of the $84 billion brought in during Q2, 2024, approximately $64.6 billion came from advertising. Most ($48.5 billion) was generated by Google Search, with another $8.6 billion from YouTube and $7.4 billion from other advertising channels. About $10.3 billion came from Google Cloud and Workspaces, with a remaining $9.3 billion from assorted services, subscriptions, devices and others, including the company’s dominant Android operating system and Google Play.
It’s important to place ad revenue in context however. Most of Google’s services rely on a free-to-use model, meaning that it doesn’t charge users directly to use its products. This includes many of its business products, such as its search and advertising data dashboards. The revenue for these products comes from advertising. Google either places ads directly, such as with Gmail and Maps, or it collects user data to place ads more effectively elsewhere. As a result, “advertising revenue” is a category that includes most of Google’s online and high-sophistication services.
Too, it’s important to remember just how big Google is. Even a small percentage of Google’s revenue represents massive amounts of money. For example, Cloud may only account for 10% of the company’s revenue, but that meant around $9 billion in one quarter alone.
A financial advisor can help you determine if Google is an appropriate investment based for you.
Google Stock Split History
Google went public via initial public offering (IPO) on August 19, 2004, with an IPO price of $85 per share (about $2.50 today, split-adjusted). Since, the company has undergone two stock splits.
- April 3, 2014: 2-for-1. Technically this split was 1,998:1,000, which is approximately 2:1. It also issued new non-voting class C shares.
- July 18, 2022: 20-for-1 split
Google Dividend History
Alphabet ($GOOG) announced its first-ever cash dividend in April 2024. The announced quarterly dividend was $0.20 per share. As of August 2024, Alphabet’s annual dividend yield is approximately 0.48%, with an annual dividend of $0.80 per share, paid quarterly. The first ex-dividend date post-announcement was set for September 9, 2024, with the payment to be made on September 16, 2024.
Before 2024, Alphabet did not pay dividends, focusing instead on reinvesting profits into growth and innovation. The decision to start paying dividends might reflect a maturation of the company.
Current Google Leadership
Alphabet, the company which owns Google, LLC, currently has a 10-person Board of Directors. It is led by CEO Sundar Pichai. Google founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin both continue to serve as Directors on Alphabet’s board. The company has a relatively small executive team though, with Ruth Porat as CFO and Amie O’Toole as CAO.
Google is one of the most valuable companies in the world. It is also one of the most dominant in its market. While statistics vary, most sources agree that somewhere between 75% and 85% of all desktop searches are made through Google and between 90% and 95% of all mobile searches. YouTube remains one of the most popular video streaming sites in the world, and is generally considered the default platform for anything longer than a brief clip. And a significant majority of all smartphones run the company’s Android operating system.
The Path Forward: Innovation and Legal Concerns
It is possible that this market dominance will spell trouble for Google, however. As noted above, the company continues to rely heavily on legacy products and services for almost all of its revenue, with all significant moneymaking products having been developed in the mid- to late-2000s. This could be the footprint of a mature firm.
More recently, like many dominant firms in the tech space, Google has become the target of antitrust concerns. At time of writing a federal judge has ruled that the company is an illegal monopoly and that it has engaged in anticompetitive practices. This was a significant ruling that targeted many of Google/Alphabet’s core business practices, with penalties that could include breaking the company up into subsidiary parts.
That said, while possible, major sanctions are unlikely. The Department of Justice has not sought a significant antitrust action since it sued Microsoft in the late 90s, and even that case resulted in a settlement that allowed the company to continue its significant business practices largely unchanged. The government hasn’t broken a company up since the dissolution of Bell in 1982. Since then, both federal courts and federal attorneys have taken an increasingly hands-off and settlement-forward approach to market regulation. This makes it possible that Google could face significant sanctions or restructuring, but unlikely.
Keep up to date on financial and economic news with the Market Minute newsletter.
The Bottom Line
Google is one of the most valuable tech companies in the world. It has a market dominance in its field that is unmatched by almost any other company in the world and a sprawling set of business and product lines in almost every part of technology.
Tips on Tech Investing
- Technology is the most valuable section of the stock market today, and it’s not even close. Six tech companies alone make up nearly a third of the value of the entire S&P 500, and when a technology company hits it can grow fast. So let’s start talking about how you can invest in tech.
- A financial advisor can help you build a comprehensive retirement plan. Finding a financial advisor doesn’t have to be hard. SmartAsset’s free tool matches you with up to three vetted financial advisors who serve your area, and you can have a free introductory call with your advisor matches to decide which one you feel is right for you. If you’re ready to find an advisor who can help you achieve your financial goals, get started now.
- Keep an emergency fund on hand in case you run into unexpected expenses. An emergency fund should be liquid — in an account that isn’t at risk of significant fluctuation like the stock market. The tradeoff is that the value of liquid cash can be eroded by inflation. But a high-interest account allows you to earn compound interest. Compare savings accounts from these banks.
- Are you a financial advisor looking to grow your business? SmartAsset AMP helps advisors connect with leads and offers marketing automation solutions so you can spend more time making conversions. Learn more about SmartAsset AMP.
Photo credit: ©iStock.com/400tmax, Google, ©iStock.com/JHVEPhoto
