Understanding what you paid for an investment is straightforward, but determining its true worth is a bit more complex. While the market value of an asset represents its current price, the intrinsic value reflects the deeper, perceived worth based on fundamental analysis. This intrinsic value is key for investors looking to gauge the true potential of their investments, especially when it comes to options. Let’s review the essentials of intrinsic value, how it applies to various assets, particularly options, and why understanding it is crucial for making informed investment decisions.
A financial advisor can help you create a financial plan for your investment needs and goals.
What Is Intrinsic Value?
Intrinsic value is the perceived value of an asset. In other words, it’s what an investor is willing to pay for a particular asset. You can calculate such value for stocks, options, a company, even real estate.
But it’s not a straightforward calculation.
Intrinsic value is determined using a variety of analyses. First, it can take a numbers-based approach. For example, when determining the intrinsic value of a company, one might consider the company’s profits, financial statements or its price-to-earnings ratio.
It can also take a more qualitative approach, using factors such as a company’s business model or its current cash flows to determine intrinsic value.
Lastly, this perceived value can also be determined by adding up a company’s assets.
It’s also worth keeping in mind that while other valuations of assets may take into account external factors, such as market conditions, intrinsic value only considers the value of the asset.
While intrinsic value and market value are similar, there are some important differences to note. Namely, the first refers to the implied value of a company, using the above analyses. However, market value refers to the value of a company as exhibited by its stock price.
Calculation
Intrinsic value can be determined through discounted cash flow (DCF) analysis, where future cash flows are estimated based on anticipated business performance.
These projected cash flows are then discounted back to their present value to estimate the intrinsic value of the company. The discount rate is typically the risk-free rate of return, often represented by the yield on a 30-year Treasury bond. Alternatively, it may also be the company’s weighted average cost of capital.
Discounted Cash Flow Formula
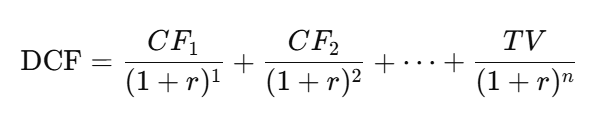
Where:
- CF = Expected cash flow for a specific period (e.g., CF1 represents the cash flow for year one)
- r = Discount rate
- TV = Terminal value (estimated cash flow beyond the projection period)
- n = The specific period (such as years, quarters or months)
Why It Matters

Intrinsic value is an important concept for investors because it allows them to see if a stock is trading below said value. That usually signifies a good investment opportunity. After all, buying low and selling high is a popular investing adage.
All investors aim to make money on their investments. Sometimes, that’s achieved via investing in an asset whose value grows over time. An investor can trade stock in a fledgling company that enjoys a period of rapid growth. Meanwhile, they can also purchase an asset that’s trading at lower than its perceived value. By selling it at a later date, they can enhance their returns.
Determining the perceived value of an asset and using it as a tool when deciding how to build your portfolio can help you maximize return on your investments. That’s why such value can be a powerful tool in an investor’s arsenal.
Intrinsic Value and Options
Intrinsic value is also an important concept when it comes to the value of options.
An option is a contract that an investor enters into that allows them — but does not require them — to buy or sell a security at a set price after a set amount of time.
So the perceived value of an option allows an investor to see the potential gains should they choose to exercise that option, or sell the asset for a set price after a predetermined amount of time.
However, unlike calculating the perceived value for asset, determining such value for an option is relatively straightforward. You can calculate it using the following formula:
Intrinsic value = (stock price – strike price) x number of options
Pros and Cons of Using Intrinsic Value
Learning an investment’s value can make you a savvier investor. Intrinsic value doesn’t just take into account the price of a particular stock, the valuation of its company or its expected return. Rather, it takes into account both numbers-based and more qualitative aspects of a particular company or asset.
However, such can be subjective. As discussed, you can determine perceived value in multiple ways. Meanwhile, you can calculate it using a variety of factors. Variables range from a company’s business model and leadership team to its financials, including long-term projections and profits.
Bottom Line

On its most basic level, the intrinsic value of an asset it what an investor is willing to pay for that asset. Investors also use it when they consider purchasing an asset. While not a straightforward calculation, the intrinsic value of an asset can help paint a picture of whether it’s a good investment with the potential for high returns.
Investment Tips
- If you’re not sure about the intrinsic value of your investments, a financial advisor may be able to help. SmartAsset’s free tool matches you with up to three vetted financial advisors who serve your area, and you can interview your advisor matches at no cost to decide which one is right for you. If you’re ready to find an advisor who can help you achieve your financial goals, get started now.
- Do you know how much investment risk you can handle? How much will your investments grow before they meet your needs? Will taxes and inflation take a bite out of your investments? SmartAsset’s investing guide can help answer these initial questions.
Photo credit: ©iStock.com/guvendemir, ©iStock.com/Anatoliy Sizov, ©iStock.com/SARINYAPINNGAM
