The SECURE 2.0 Act has opened a new door for burdened student loan borrowers by offering a side door to achieving loan payoff and making crucial retirement contributions as soon as possible. But many are still left confused about this new legislation.
Below we’ll unpack the details, but you should consider introducing a financial advisor to your financial strategy for a more in-depth review of how these changes can directly impact your future and financial goals.
The SECURE 2.0 Act Summary
The SECURE 2.0 Act, passed as part of the Biden administration’s $1.7 trillion omnibus spending bill in December, aims to make a secure retirement more achievable for Americans. In short, it has options that will help those who struggle with saving for retirement hit their financial goals without having to sacrifice paying off debt or postpone saving for a home. This includes:
- Mandatory auto-enrollment into company-sponsored retirement plans
- Increase annual catch-up limits for contributors age 50+
- Roth matching as a contribution option
- Raising the minimum age for compulsory minimum distribution elections
- Increase part-time employee participation in retirement savings plans
And of course the hot topic – student loan matching.
What Is the Student Loan Matching Component of the SECURE 2.0 Act?
Student loan matching allows companies to match their employee’s student loan payments with retirement contributions. This is big news since prior to the SECURE 2.0 Act, companies were limited to only offering a match to their employee’s retirement contributions.
Let’s look at an example.
The situation: To give a better visual imagine Dave, a fresh college graduate with student loan debt starts a new job that offers a salary plus benefits. One of the benefits is a 3% company match. Traditionally this match applies to his retirement contribution, so when Dave contributes 3% of his salary to his company-sponsored 401(k), he’s met with an additional 3% from his company.
The problem: When Dave contributes to his 401(k), it puts him in a great spot for retiring on time down the road, but he now can’t afford to save for a house and pay down his student loan debt at the same time. He has to choose one or the other. One leaves him as a prolonged renter spending money on an asset that he’ll never own; the other leaves him extending student loan payoff and accruing additional interest.
The solution: Student loan matching allows his company to match his student loan payments instead of a retirement contribution. So the result looks like this:
- Dave is able to pay down his student loans avoiding additional interest charges.
- Dave can get a jump start on saving for a home preserving thousands on potential rent.
- Dave gets a compounding effect from his company’s retirement plan contributions.
As you can see, this match option has long-reaching potential.

Why Is Student Loan Matching Important?
Effectively saving for retirement has been a longstanding (and growing) issue nationwide, but student loan matching offers a method of solving two problems at the same time.
With student loan matching, companies can contribute to your retirement savings so you still receive the ever-so-important compounding effect while also being able to pay down your student loan debt.
Another way to consider it– the government is putting a much-needed incentive in place that helps student loan borrowers pay down debt faster.
Who Qualifies for Student Loan Matching?
The beneficiary of the student loan is qualified to receive student loan matching from their employer. The details are both vague and intricate but here’s what we know for sure based on the official SECURE 2.0 Act document.
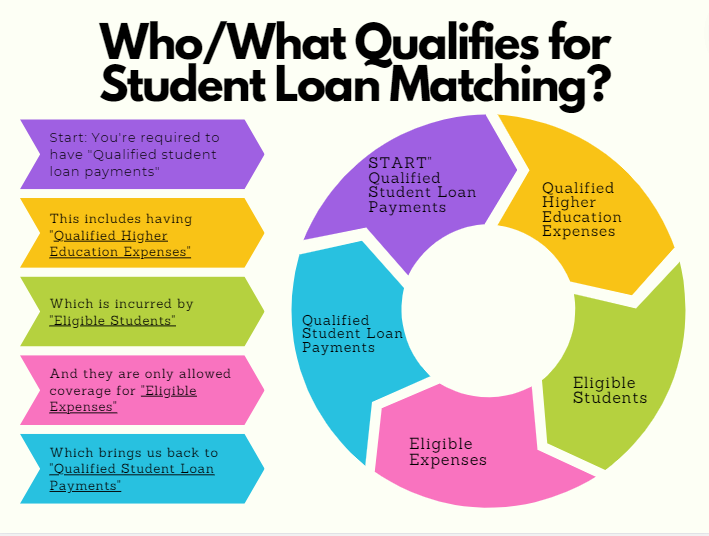
The flow is a bit obscure (as is tax code with the IRS), so here’s a graphic to break it down followed by the text to further explain the web of requirements in detail:
The official text reads “Section 110 permits an employer to make matching contributions under a 401(k) plan, 403(b) plan, or SIMPLE IRA with respect to “qualified student loan payments.”
- “Qualified student loan payments” are defined by the IRS as a loan taken out for the sole purpose of paying for a qualified higher education expense for:
– You, your spouse or your dependent when you took out the loan
– Education during an academic period for an eligible student and paid (received) within a reasonable period time before or after you took the loan out. - “Qualified higher education expenses” are defined by the IRS as tuition, fees or other related expenses for an eligible student.
- “Eligible student” is defined by the IRS as an individual who is enrolled at least half-time (6 credits) in a program of study leading to a degree, certificate, or other recognized educational credential at an eligible educational institution.
- “Eligible expenses” are defined by the IRS as required student activity fees, books or anything that is required to enroll or attend the school.
Eligible Expenses Exclusions For Student Loan Matching?
Expenses that don’t qualify are:
- Non-credit courses
- Sports
- Games
- Hobbies
- Room & board
- Insurance
- Medical expenses (including health fees)
- Transportation
Can I Still Receive Student Loan Matching If I Didn’t Graduate?
The Secure 2.0 Act doesn’t specify that graduation was required. Only that it be a “qualified student loan payment.” However, this may be up to your employer if you can still participate without completing a degree for the loans you incurred.
Similar programs like Student Loan Forgiveness do not require completion to receive their benefit so it stands to reason that this benefit won’t either.
The Bottom Line
The majority of people that have incurred student loan debt are eligible for the student loan matching program; however, it is up to the employer if you’re offered this as a benefit.
Tips for Retirement
- Finding a financial advisor doesn’t have to be hard. SmartAsset’s free tool matches you with up to three vetted financial advisors who serve your area, and you can interview your advisor matches at no cost to decide which one is right for you. If you’re ready to find an advisor who can help you achieve your financial goals, get started now.
- Want to see if you’ll have enough money for retirement. Use SmartAsset’s retirement calculator.
Photo credit: ©iStock.com/DNY59, Photo credit: ©iStock.com/idealistock